Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Finding Values Of A Normally Distributed Random Variable Calculator
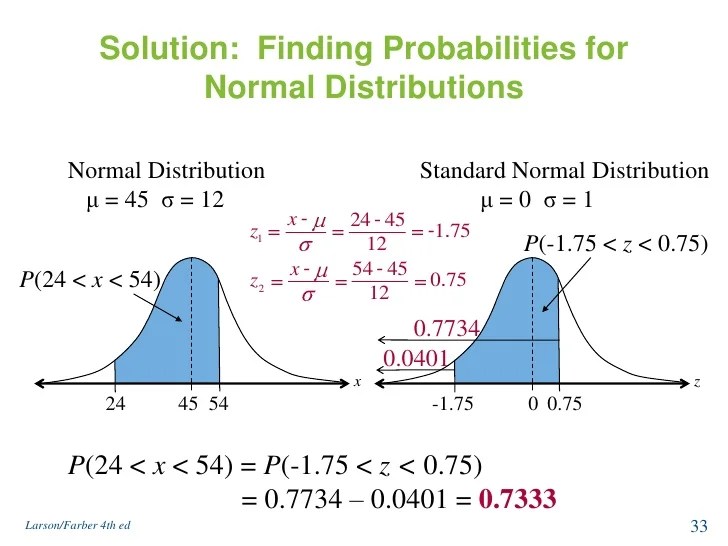
Finding Values Of A Normally Distributed Random Variable Calculator. We can use the following process to find the probability that a normally distributed random variable x takes on a certain value, given a mean and standard deviation: About 95% of the values lie within two standard deviations;
The calculator below gives quantile value by probability for the specified. The default value μ and σ shows the standard normal distribution. Where μ = mean of the population of the x value and σ = standard deviation for the population of the x value.
About 68% Of Values Drawn From A Normal Distribution Are Within One Standard Deviation Σ Away From The Mean;
The answer is simple, the standard normal distribution is the normal distribution when the population mean \mu μ is 0 and the population standard deviation is \sigma σ is 1. (6.3.1) z = x − μ σ. The probability density function for a normally distributed random variable x with mean μ and standard deviation σ is given by:
The F (Fisher Snedecor) Distribution Is Used For A Normally Distributed Population.
For a continuous probability distribution, probability is calculated by taking the area under the graph of the probability density function, written f (x). F x ( x, μ, σ) = 1 σ 2 π e − ( x − μ 2). Where μ = mean of the population of the x value and σ = standard deviation for the population of the x value.
More Data Exist Around The Center, Which Is The Average, And As Further The Value Is From The Center The Less Likely It Occurs.
Using a table of values for the standard normal distribution, we find that. Since you want to learn methods for computing expectations, and you wish to know some simple ways, you will enjoy using the moment generating function (mgf) $$\phi(t) =. Normal or gaussian distribution (named after carl friedrich gauss) is one of the most important probability distributions of a continuous random variable.
Thus, There Is A 0.6826 Probability That The.
Where x is a normal random. This function is called the probit function. If you selected the inverse normal distribution calculator, you enter the probability given by the exercise, depending on whether it is the upper or lower tail.
A Normally Distributed Random Variable Has A Mean Of And A Standard Deviation Of.
The normal distribution is important. Where x is a normal random variable, μ is the mean of x, and σ is the. About 95% of the values lie within two standard deviations;
Comments
Post a Comment